Introduction: Ethanol Blending Is More Than Fuel
India’s ethanol blending program has grown far beyond its original goal of mixing ethanol with petrol. What started as a move to cut fuel imports has now become a strong driver of industrial growth across multiple sectors. Today, ethanol touches agriculture, bio-energy, chemicals, animal nutrition, and logistics—making it a powerful foundation for new manufacturing businesses.
Modern distilleries are no longer single-purpose units. They function as integrated industrial facilities that produce fuel ethanol along with valuable by-products such as animal feed, carbon dioxide, bio-energy, and chemical inputs. This shift has created multiple revenue streams and reduced business risk.
For entrepreneurs and startups, ethanol-linked manufacturing offers something rare: policy support, long-term demand, and scalable business models that banks and institutions are willing to fund.
Why the Ethanol Blending Program Is Important for Business Owners
The ethanol blending initiative supports three major national objectives:
- Reducing dependence on imported crude oil
- Ensuring steady income for farmers
- Building domestic, bio-based manufacturing capacity
What makes this opportunity attractive is that the government plays the role of facilitator, not operator. The actual execution is driven by private companies, MSMEs, and regional manufacturers, backed by assured buyers like oil marketing companies.
Unlike many policy-led sectors that remain on paper, ethanol blending is already in the execution phase. Capacities are expanding, supply chains are maturing, and real business opportunities are being created—this is where entrepreneurs gain the most.
 How Rising Ethanol Demand Is Reshaping Industry
How Rising Ethanol Demand Is Reshaping Industry
Growing ethanol demand has triggered several structural changes in Indian manufacturing, including:
- Expansion of grain-based and sugar-based distilleries
- Use of multiple agricultural feedstocks instead of only molasses
- Development of by-product processing units
- Strong linkages with farming communities
- New downstream industries in fuels, chemicals, and bio-inputs
Ethanol has evolved from a single commodity into a platform industry that supports multiple manufacturing activities.
Feedstock Diversification: Opening Doors Across India
Earlier, ethanol production depended mostly on molasses from sugar mills. Today, producers use a wide range of raw materials, such as:
- Sugarcane juice and B-heavy molasses
- Maize and broken rice
- Damaged and surplus food grains
- Other excess agricultural produce
This change has two major advantages for entrepreneurs:
- Ethanol plants can now be set up beyond traditional sugar belts
- Grain-based and flexible-feedstock distilleries are suitable for MSME-scale investment
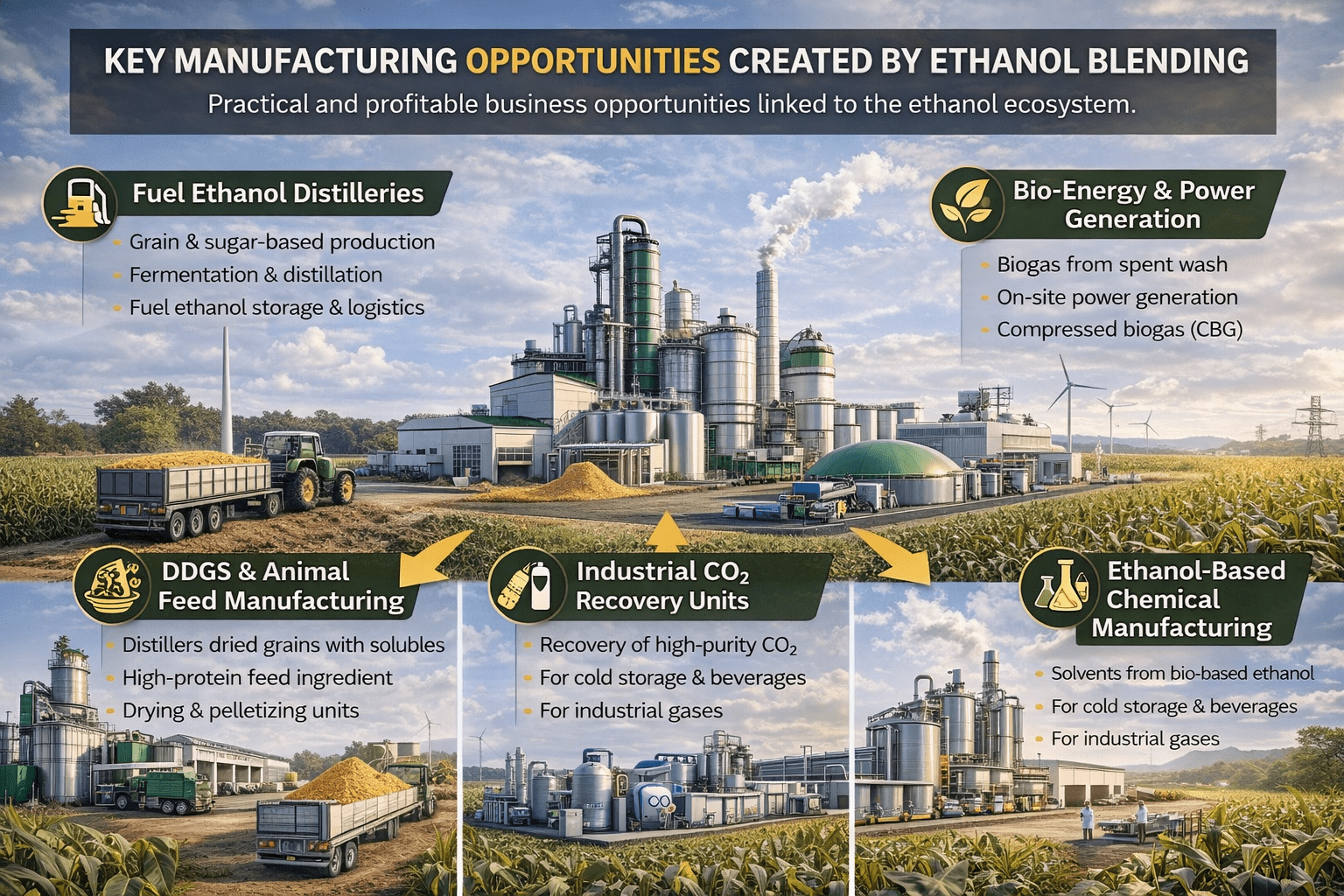
Key Manufacturing Opportunities Created by Ethanol Blending
Below are some of the most practical and profitable business opportunities linked to the ethanol ecosystem.
-
Fuel Ethanol Distilleries (Grain & Sugar-Based)
Fuel ethanol production is the backbone of the blending program. Today’s distilleries operate as advanced processing plants that convert farm produce into standardized fuel.
Main activities include:
- Raw material handling and milling
- Fermentation and distillation
- Dehydration to fuel-grade ethanol
- Storage and logistics
Entrepreneurs are entering this sector because pricing is structured, buyers are assured, and capacity can be expanded gradually. Ongoing investments across India indicate long-term stability in this segment.
-
DDGS and Animal Feed Manufacturing
Distillers Dried Grains with Soluble (DDGS) is a high-protein by-product generated from grain-based ethanol plants. Earlier treated as waste, DDGS is now a valuable feed ingredient.
Key markets include:
- Poultry feed
- Dairy and cattle feed
- Aquaculture feed
Since there is no extra fermentation cost, DDGS offers attractive margins. Many MSMEs are setting up dedicated drying, pelletizing, and packaging units connected to distilleries.
-
Industrial CO₂ Recovery Units
During fermentation, ethanol plants release high-purity carbon dioxide. Instead of releasing it into the atmosphere, this CO₂ can be captured and sold.
Uses include:
- Food and beverage processing
- Welding and industrial gases
- Cold storage and refrigeration
- Chemical manufacturing
CO₂ recovery units require relatively low investment and benefit from strong industrial demand, making them a smart add-on business.
-
Bio-Energy and Power Generation
Distillery waste such as spent wash and organic residue can be used to generate biogas and electricity.
Business models include:
- Biogas plants
- Captive power generation
- Integration with compressed biogas (CBG)
These systems reduce energy costs and create additional income while supporting environmental compliance.
-
Ethanol-Based Chemical Manufacturing
Ethanol is also an important raw material for many industries.
Downstream applications include:
- Acetic acid and ethyl acetate
- Industrial solvents
- Pharmaceuticals and personal care products
Entrepreneurs can explore ethanol-based chemical plants, solvent production, or contract manufacturing for larger chemical companies, especially as demand for bio-based inputs grows.
 Green Fuel: The Strategic Backbone of India’s Energy Transition
Green Fuel: The Strategic Backbone of India’s Energy Transition
Green fuel has emerged as a central pillar of India’s long-term energy and industrial strategy. As climate commitments tighten and fossil fuel volatility increases, ethanol-based green fuel is no longer just an alternative—it is becoming a necessity. Ethanol blending represents one of the most practical and scalable green fuel solutions available today, especially for a developing economy like India.
Unlike electric mobility or hydrogen, which require massive infrastructure changes, ethanol-based green fuel integrates seamlessly with existing fuel distribution systems. This compatibility makes ethanol one of the fastest pathways for India to reduce carbon emissions while maintaining energy security.
For manufacturers and entrepreneurs, green fuel is not merely an environmental concept—it is a commercially viable, policy-backed industrial opportunity.
Why Ethanol Is Considered a Scalable Green Fuel
Ethanol qualifies as a green fuel because it is derived from renewable agricultural resources and significantly reduces lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil petrol. When produced responsibly, ethanol-based green fuel contributes to:
- Lower carbon intensity in transportation
- Reduced particulate and sulfur emissions
- Circular utilization of agricultural surplus
- Rural employment and income generation
What sets ethanol apart from other green fuels is its scalability. Feedstock flexibility, distributed production, and assured offtake make ethanol uniquely suited to India’s economic structure.
This scalability ensures that green fuel production is not limited to large corporations—MSMEs and regional manufacturers can actively participate.
Green Fuel and Rural Industrialization
One of the most overlooked advantages of green fuel manufacturing is its ability to decentralize industrial growth. Ethanol plants are often located near agricultural hubs, creating localized value chains.
Green fuel-driven rural industrialization results in:
- Reduced transportation costs for feedstock
- Stable demand for farm produce
- Creation of allied industries such as logistics, storage, and packaging
- Employment for semi-skilled and skilled rural labor
As green fuel demand increases, rural districts are emerging as new industrial clusters rather than raw-material suppliers alone.
Integration of Green Fuel with Circular Economy Models
Ethanol-based green fuel fits naturally into a circular economy framework. Very little from an ethanol plant goes to waste.
Circular value streams include:
- DDGS for animal nutrition
- CO₂ capture for industrial reuse
- Biogas from spent wash
- Organic manure from bio-slurry
This multi-output structure enhances resource efficiency and improves profitability while ensuring environmental compliance.
Entrepreneurs who design ethanol projects with circular economy integration gain a competitive advantage in cost, sustainability, and regulatory approvals.
Green Fuel as a Hedge Against Energy Price Volatility
Global crude oil prices are subject to geopolitical tensions and supply disruptions. Green fuel production provides insulation against these uncertainties.
For India, expanding domestic green fuel capacity helps:
- Stabilize fuel supply chains
- Reduce foreign exchange outflow
- Improve energy self-reliance
For businesses, green fuel offers long-term pricing visibility through government procurement mechanisms. This predictability is particularly attractive for lenders, investors, and financial institutions.
 Technology Advancements Strengthening Green Fuel Economics
Technology Advancements Strengthening Green Fuel Economics
Recent technological improvements have significantly enhanced the economics of green fuel manufacturing.
Key advancements include:
- High-efficiency fermentation enzymes
- Multi-feedstock distillation technology
- Energy-efficient dehydration systems
- Automated process control and monitoring
These improvements reduce per-unit production costs, improve yields, and make even mid-scale green fuel projects commercially viable.
Technology-driven efficiency is now a decisive factor separating successful ethanol ventures from underperforming ones.
Green Fuel and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Alignment
ESG considerations are increasingly influencing investment decisions. Green fuel manufacturing aligns strongly with ESG frameworks.
From an ESG perspective, ethanol-based green fuel delivers:
- Environmental benefits through emission reduction
- Social benefits through farmer income and rural jobs
- Governance benefits through regulated procurement and compliance
Companies involved in green fuel manufacturing are better positioned to attract institutional capital, impact investors, and green financing instruments.
Role of Green Fuel in India’s Net-Zero Commitments
India’s commitment to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070 places green fuel at the center of future energy planning. Ethanol blending offers immediate emission reduction without waiting for disruptive technologies to mature.
Green fuel adoption helps bridge the transition phase between fossil dependency and next-generation energy systems such as hydrogen and advanced biofuels.
This transitional role ensures long-term relevance and policy continuity for ethanol-based green fuel projects.
Green Fuel and MSME-Led Manufacturing Growth
The green fuel ecosystem actively encourages MSME participation across the value chain.
MSME-friendly segments include:
- Grain-based ethanol distilleries
- DDGS processing and packaging units
- CO₂ bottling and distribution
- Bio-energy and CBG plants
- Green fuel logistics and storage
These segments require moderate capital, offer predictable demand, and benefit from established buyers, making them ideal for first-generation entrepreneurs.
Financing Advantages for Green Fuel Projects
Banks and financial institutions increasingly prioritize green fuel projects due to their lower risk profile and government backing.
Financing advantages include:
- Priority sector lending eligibility
- Interest subvention schemes
- Long-term offtake assurance
- Higher acceptance of DPR-based lending
Well-structured green fuel projects with integrated by-product monetization demonstrate stronger debt servicing capability and faster break-even.
Export Opportunities Linked to Green Fuel Ecosystem
As global demand for sustainable fuels and bio-based products increases, India’s green fuel ecosystem opens export possibilities.
Export-linked opportunities include:
- DDGS for international feed markets
- Bio-based solvents and chemicals
- Ethanol plant machinery and technology
- Engineering and EPC services
Green fuel exports enhance India’s positioning as a responsible and competitive bio-manufacturing hub.
Strategic Considerations for New Green Fuel Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs entering the green fuel sector should focus on strategic planning rather than scale alone.
Key success factors include:
- Feedstock security and diversification
- Energy integration and waste utilization
- Compliance-ready plant design
- Conservative financial assumptions
- Phased capacity expansion
Green fuel projects reward operational discipline and long-term vision more than aggressive scaling.
Future Outlook: Green Fuel Beyond Ethanol Blending
While ethanol blending is currently the anchor, green fuel applications will expand into:
- Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF)
- Advanced biofuels
- Green chemicals and materials
- Hybrid energy systems
Entrepreneurs who enter the ethanol ecosystem today gain early access to future green fuel value chains.
Final Perspective: Green Fuel as an Industrial Opportunity
Green fuel is no longer an experimental or niche concept—it is a mainstream industrial reality. Ethanol blending has proven that green fuel can deliver economic growth, environmental responsibility, and energy security simultaneously.
For entrepreneurs, manufacturers, and investors, green fuel represents a rare convergence of policy support, market demand, and scalable technology.
Those who build capabilities now will not only participate in today’s ethanol market but will also shape India’s broader green fuel future.
Import Reduction and Export Potential
Ethanol-linked manufacturing helps India reduce imports of:
- Petroleum fuels
- Chemical intermediates
- Protein-rich animal feed
At the same time, export opportunities are emerging in DDGS, bio-based chemicals, and ethanol plant technology, strengthening the overall investment case.
Why This Sector Works for New Entrepreneurs
Ethanol-linked businesses stand out because they offer:
- Policy-backed and predictable demand
- Renewable, agriculture-based raw materials
- Established and creditworthy buyers
- Multiple income streams from one facility
These factors make ethanol manufacturing less speculative and more stable compared to many other industries.
Lessons from Successful MSMEs
Many successful MSME promoters in this sector followed simple strategies:
- Starting with manageable capacities
- Monetizing by-products from day one
- Focusing on efficiency and compliance
- Gradually integrating forward and backward
Several small operators have grown into fully integrated bio-manufacturing companies, proving the scalability of the ecosystem.
How NPCS Helps Entrepreneurs Succeed
Ethanol projects require careful planning due to high capital investment and regulatory requirements. At Niir Project Consultancy Services (NPCS), we help entrepreneurs make informed decisions before investing.
Our Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) include:
- Manufacturing processes and technology
- Market demand and competition analysis
- Process flow diagrams
- Machinery and raw material planning
- Complete financial projections and profitability analysis
Our goal is to reduce risk and improve project success through realistic, data-driven planning.
Institutional Support Framework
The ethanol ecosystem is supported by multiple government bodies, including:
- Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas
- Ministry of Food and Public Distribution
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare
- Oil Marketing Companies
Together, these institutions ensure policy stability, assured procurement, and long-term ecosystem growth.
Quick Opportunity Overview
|
Segment |
Product | Market | Startup suitability |
|
Distillery |
Fuel | Oil companies | Medium-High |
|
DDGS |
Animal Feed |
Poultry & dairy | Very High |
| CO₂ Recovery | Industrial | Food & welding |
High |
| Bio-Energy | Biogas/power | Captive use |
High |
| Chemicals | Solvents | Industry |
Medium |
Why the Timing Is Right
The ethanol sector has moved from rapid expansion to optimization. The next phase will reward entrepreneurs who focus on efficiency, integration, and by-product value.
Those entering now are not late—they are arriving at the stage where smart execution creates long-term leadership.
How NIIR Project Consultancy Services (NIIR.org) Supports Entrepreneurs
Ethanol projects involve high capital investment and regulatory complexity. NIIR Project Consultancy Services (NIIR.org) helps entrepreneurs reduce risk and improve success rates through structured project planning.
NIIR’s Support Includes:
- Identification of viable ethanol-linked business models
- Detailed market demand and pricing analysis
- Technology selection and process design
- Machinery, utilities, and raw material planning
- Environmental and compliance considerations
- Comprehensive Techno-Economic Feasibility Reports (DPRs)
- Financial projections, IRR, DSCR, and break-even analysis
NIIR’s DPRs are widely accepted by banks, NBFCs, investors, and government agencies.
Institutional & Government Support Framework
The ethanol ecosystem is supported by multiple government institutions, including:
- Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas – https://mopng.gov.in
- Department of Food & Public Distribution – https://dfpd.gov.in
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare – https://agricoop.nic.in
- Oil Marketing Companies (IOCL, BPCL, HPCL)
- NITI Aayog – https://www.niti.gov.in
These bodies ensure policy continuity, assured procurement, and ecosystem stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is ethanol manufacturing suitable for MSMEs?
Yes. Grain-based distilleries, DDGS units, CO₂ recovery, and bio-energy projects are suitable for MSME-scale investments.
Q2. Are buyers assured for ethanol?
Yes. Oil Marketing Companies procure ethanol under long-term government-backed programs.
Q3. Is a DPR mandatory for ethanol projects?
A DPR is essential for bank financing, regulatory approvals, and investment planning.
Q4. Can ethanol plants operate on multiple feedstocks?
Yes. Modern distilleries are designed for flexible feedstock usage.
Q5. How does NIIR reduce project risk?
NIIR provides realistic, data-driven project reports covering technology, finance, market demand, and compliance.
Final Thought
India’s ethanol blending programmed is transforming more than the fuel market—it is building a future-ready bio-manufacturing ecosystem. Entrepreneurs who move beyond basic distillation and adopt integrated, multi-product models can create resilient, scalable, and profitable businesses.
For investors and startups seeking policy alignment, long-term demand, and sustainable growth, ethanol-linked manufacturing represents one of India’s strongest industrial opportunities—and with expert guidance from NIIR Project Consultancy Services (NIIR.org), this opportunity can be converted into lasting success.

















