Introduction: India at the Start of a Manufacturing Breakthrough
India is entering a decisive phase in its industrial journey. The period between 2025 and 2030 is widely expected to become one of the most important growth cycles for Indian manufacturing in recent decades.
Multiple forces are aligning at the same time—strong domestic consumption, renewed investor confidence, global companies diversifying supply chains toward India, rapid adoption of automation and artificial intelligence, and sustained government focus on industrial growth. Together, these factors are creating a once-in-a-generation opportunity for entrepreneurs to build scalable, resilient, and globally competitive manufacturing businesses.
Manufacturing in India is no longer expanding cautiously. It is moving forward with confidence, capital backing, and a long-term strategic vision.
Why 2025–2030 Is a Defining Window for Manufacturing Entrepreneurs
1. A More Supportive and Stable Economic Environment
India’s business environment has become significantly more favorable for new industrial ventures. Banks are well-capitalized, corporate balance sheets are stronger, and consumption is rising across urban and rural markets.
For manufacturing startups, this translates into:
- Better access to institutional credit
- Stronger demand from large buyers and EPC players
- Improved payment cycles
- Rising B2B, infrastructure, and industrial spending
Compared to earlier decades, the ecosystem today is far more welcoming for first-time and growth-stage manufacturers.
2. Rapid Transition Toward Smart Manufacturing
Indian factories are modernizing faster than ever before. Technologies such as AI-driven quality inspection, robotics, predictive maintenance, and digital production monitoring are being adopted across industries like automotive, electronics, chemicals, steel, and engineering.
This transition is creating new opportunities in:
- Automation and control components
- Industrial sensors and IoT hardware
- AI-enabled inspection and testing systems
- Robotics integration and industrial services
Manufacturing startups that combine production capability with technology adoption will hold a strong competitive edge during this decade.
3. Global Companies Are Deepening Their Manufacturing Presence in India
International companies are increasingly choosing India as a preferred manufacturing and sourcing destination. Large investments are flowing into electronics, electric vehicles, renewable energy, data centres, logistics, and industrial engineering.
This expansion creates opportunities for Indian MSMEs in:
- Component manufacturing
- Contract and precision manufacturing
- Fabrication and assembly
- Utilities, maintenance, and industrial support services
When global companies invest, they also build extensive local supplier networks—this is where manufacturing startups can scale rapidly.
4. Import Dependence Is Opening Large Domestic Markets
India continues to import significant volumes of:
- Electronic components
- Specialty and performance chemicals
- Industrial machinery and equipment
- EV parts and power electronics
- Solar and energy-storage equipment
Reducing import dependence is now a strategic national objective. Startups that manufacture these products locally can benefit from assured demand, policy incentives, and long-term market stability.
Import substitution is expected to be one of the largest value-creation themes for Indian manufacturing between 2025 and 2030.
5. Manufacturing-Focused Government Policies
Government initiatives such as:
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes
- Capital goods and engineering sector support
- EV and green-energy promotion
- Atmanirbhar Bharat mission
have placed manufacturing at the centre of India’s growth strategy. Entrepreneurs today receive stronger policy backing, infrastructure support, and incentive alignment than ever before.
High-Growth Manufacturing Sectors for 2025–2030
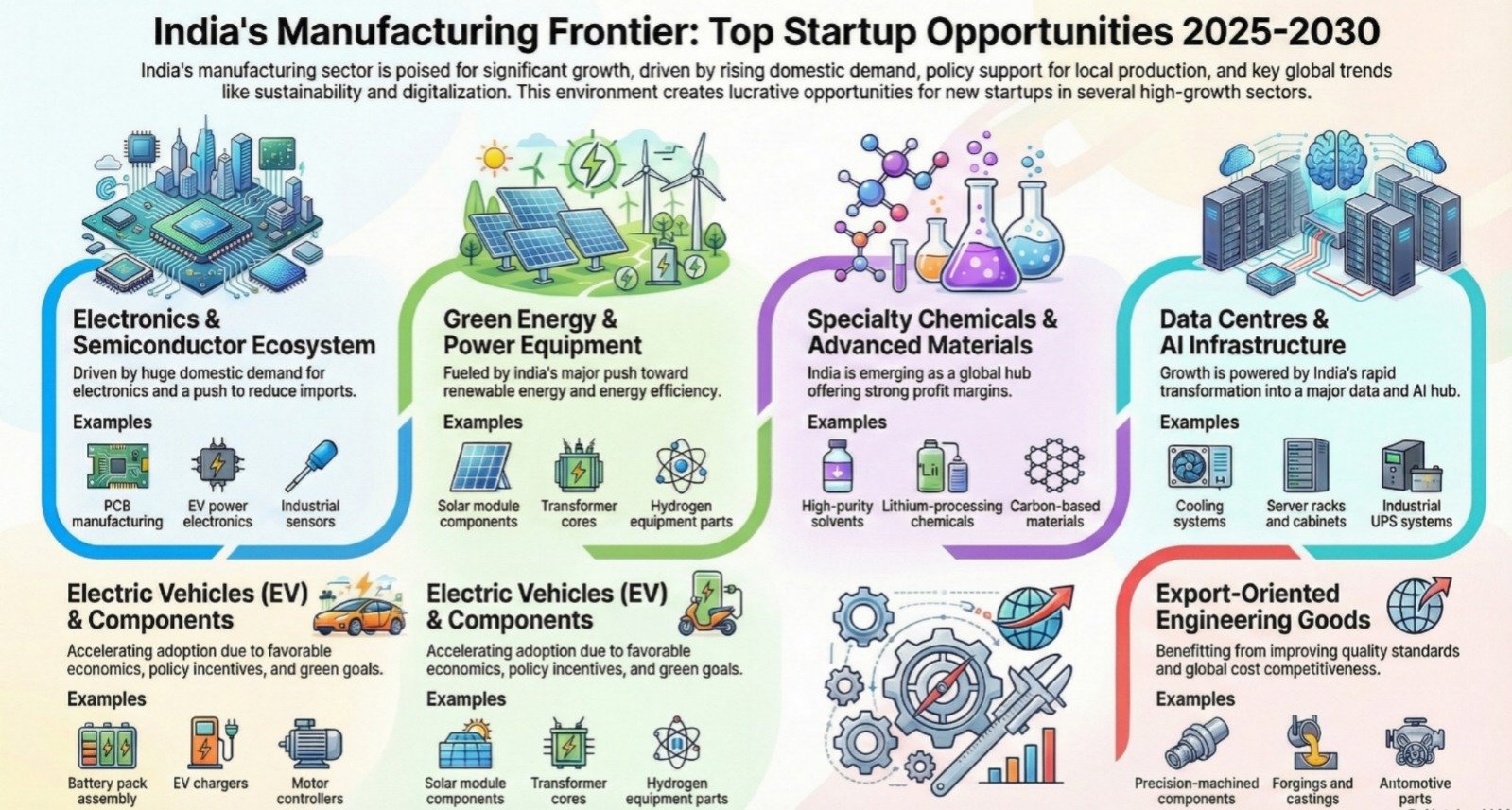
1. Electronics and Semiconductor Ecosystem
Why this sector will expand rapidly
India imports a large share of its electronics while domestic demand for smartphones, EV electronics, industrial automation, and IoT devices continues to rise.
Startup opportunities include:
- PCB manufacturing
- Semiconductor packaging and testing
- LED drivers and power supplies
- EV power electronics
- Industrial sensors and modules
This sector offers both domestic scale and export potential.
2. Green Energy and Power Equipment
India’s push toward renewable energy, green hydrogen, and energy-efficient infrastructure is driving demand for locally manufactured equipment.
Manufacturing opportunities:
- Solar module components
- Transformer cores and laminations
- Hydrogen equipment parts
- Power cables and switchgear
Many of these components are still imported, creating room for domestic players.
3. Electric Vehicles and EV Components
EV adoption is accelerating due to fuel economics, policy incentives, and sustainability goals.
High-potential startup areas include:
- Battery pack assembly
- EV chargers
- Motor controllers and inverters
- Wiring harnesses
- Structural and metal components
Localisation in EV manufacturing is still at an early stage.
4. Specialty Chemicals and Advanced Materials
India is emerging as a global hub for specialty chemical manufacturing.
Profitable segments include:
- High-purity solvents
- Epoxy resins
- Lithium-processing chemicals
- Carbon-based materials
- Advanced fillers and silica products
With proper compliance and quality systems, this sector offers strong margins.
5. Engineering Fabrication and Capital Goods
Infrastructure expansion and industrial modernisation are creating sustained demand for engineering products.
Startup options include:
- Metal fabrication
- Industrial valves and pumps
- Transmission and tower structures
- Material-handling equipment
- Welding consumables
These businesses benefit from long-term industrial demand cycles.
6. Agro-Based and FMCG Manufacturing
India’s population growth and expanding retail networks continue to support agro-processing industries.
Manufacturing ideas include:
- Maize starch and derivatives
- Bio-CNG
- Cold-storage solutions
- Ready-to-eat food products
- Edible oil refining
Agro-based manufacturing also supports rural income generation.
7. Data Centres and AI Infrastructure
India is becoming a major data and AI hub.
Manufacturing opportunities include:
- Cooling and HVAC systems
- Power backup equipment
- Server racks and cabinets
- Industrial UPS systems
- Electrical and cabling solutions
8. Logistics, Warehousing, and Material Handling
Growth in e-commerce, aviation, and infrastructure is expanding logistics demand.
Manufacturing scope includes:
- Conveyors and pallets
- Storage and warehouse racks
- Forklifts and stackers
- Cold-chain equipment
- AGV components
9. Export-Oriented Engineering Goods
Indian engineering exports are growing due to improving quality and cost competitiveness.
Startup opportunities include:
- Fasteners
- Precision-machined components
- Forgings and castings
- Automotive parts
- Industrial tools
Exports add scale and foreign-exchange earnings.
Below is the additional content only, written in the same structured format, tone, and depth, and naturally optimized around the keyword “Indian Manufacturing Startups.” You can append this directly to your existing article.
 Additional Growth Drivers Strengthening Indian Manufacturing Startups (2025–2030)
Additional Growth Drivers Strengthening Indian Manufacturing Startups (2025–2030)
1. Infrastructure Expansion Is Creating Manufacturing Demand at Scale
India’s massive infrastructure pipeline is acting as a powerful demand engine for Indian manufacturing startups. Large-scale investments in highways, railways, ports, airports, metro projects, smart cities, water treatment, and industrial corridors are translating directly into sustained demand for manufactured goods.
Key manufacturing opportunities emerging from infrastructure expansion include:
- Construction chemicals and admixtures
- Electrical equipment, cables, and switchgear
- Pre-engineered building components
- Pipes, valves, and fittings
- Safety equipment and industrial consumables
Unlike short-term consumer trends, infrastructure-led demand is long-term and predictable. Indian manufacturing startups that align their product portfolios with infrastructure projects benefit from repeat orders, volume stability, and lower market volatility.
2. Rising Role of MSMEs in Large Industrial Value Chains
Large Indian conglomerates and multinational corporations are increasingly outsourcing manufacturing to specialized MSMEs. This shift is driven by cost efficiency, focus on core competencies, and the need for flexible supplier ecosystems.
Indian manufacturing startups are finding strong opportunities in:
- Tier-2 and Tier-3 component manufacturing
- Job work and precision subcontracting
- Custom-engineered industrial solutions
- Vendor development programs of PSUs and EPC firms
Government policies now actively promote MSME participation in public procurement, defense manufacturing, railways, and energy projects. This integration into formal supply chains improves credit access, payment security, and long-term business sustainability for startups.
3. Defense and Aerospace Manufacturing: A New Frontier
India’s defense manufacturing ecosystem is undergoing a structural transformation. With rising defense budgets and a strong push for indigenization, Indian manufacturing startups are entering areas that were once dominated by imports.
High-potential segments include:
- Defense electronics and communication systems
- Precision machined components
- Aerospace-grade fasteners and alloys
- Composite materials and assemblies
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) components
Defense manufacturing offers long-term contracts, stable demand, and strong government backing. While entry barriers exist in terms of certification and compliance, startups that invest early gain a durable competitive advantage.
4. Digital India and Industry 4.0 Are Reshaping Manufacturing Models
Digital transformation is no longer limited to large factories. Indian manufacturing startups are increasingly adopting Industry 4.0 principles from day one, allowing them to operate leaner and smarter than legacy players.
Key advantages include:
- Digital design and simulation reducing development time
- Smart inventory and supply-chain management
- Real-time production tracking and analytics
- Improved traceability and compliance
By embedding digital tools early, startups can achieve higher productivity, better quality control, and faster scalability without proportional increases in manpower or capital expenditure.
5. Skilled Workforce Availability and Industrial Training Ecosystem
India’s demographic advantage is translating into a growing pool of technically trained manpower. Initiatives such as Skill India, ITI modernization, and industry-academia collaboration are improving workforce readiness.
For Indian manufacturing startups, this means:
- Easier access to shop-floor technicians
- Lower training costs over time
- Availability of specialized skills in welding, CNC, automation, and quality control
- Growing talent pool for R&D and process engineering
Several states are also offering skill-linked incentives, apprenticeship support, and wage subsidies for manufacturing units, reducing operational costs for startups.
6. State-Level Manufacturing Policies and Industrial Clusters
Beyond central government schemes, state governments are aggressively competing to attract manufacturing investments. Many states have developed sector-specific industrial clusters that reduce entry barriers for startups.
Benefits of cluster-based manufacturing include:
- Shared infrastructure and utilities
- Proximity to suppliers and customers
- Faster regulatory approvals
- Access to common testing and certification facilities
States such as Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Telangana, Odisha, and Uttar Pradesh are offering customized incentives for Indian manufacturing startups, especially in electronics, EVs, chemicals, and engineering goods.
7. Export Competitiveness and Trade Agreements
India’s manufacturing exports are becoming more competitive due to improved quality standards, cost efficiency, and trade diplomacy. Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and bilateral trade partnerships are opening new markets for Indian manufacturers.
Export-oriented Indian manufacturing startups can benefit from:
- Access to diversified global markets
- Foreign exchange earnings
- Reduced dependence on domestic demand cycles
- Higher valuation multiples for export-led businesses
Sectors such as engineering goods, auto components, chemicals, textiles, and electronics are particularly well-positioned to scale through exports during 2025–2030.
8. Sustainability, ESG, and Green Manufacturing Advantage
Sustainability is becoming a business requirement rather than a compliance obligation. Indian manufacturing startups that integrate energy efficiency, waste reduction, and ESG practices early gain preference from global buyers and investors.
Opportunities linked to green manufacturing include:
- Energy-efficient machinery and components
- Recycling and circular-economy products
- Low-emission materials and processes
- Water treatment and zero-liquid-discharge systems
Green manufacturing not only improves brand credibility but also reduces operating costs over the long term.
9. Financing Ecosystem Is More Mature Than Ever
Access to finance has historically been a challenge for manufacturing entrepreneurs. Today, the ecosystem has evolved significantly.
Indian manufacturing startups now have access to:
- Specialized MSME lending institutions
- Venture debt and private credit funds
- Government-backed credit guarantee schemes
- SIDBI and state financial corporation support
In addition, professionally prepared DPRs and feasibility studies are improving approval rates for loans and investor funding.
10. Importance of Structured Project Planning for Manufacturing Startups
While opportunities are abundant, success in manufacturing depends heavily on planning discipline. Indian manufacturing startups that invest time in structured project planning outperform those that rely on intuition alone.
Critical planning elements include:
- Realistic capacity selection
- Accurate cost estimation
- Technology benchmarking
- Regulatory and environmental compliance
- Financial stress testing
Professional project planning reduces execution risk and improves long-term profitability.
Strategic Advice for Indian Manufacturing Startups Entering This Decade
Entrepreneurs entering manufacturing between 2025 and 2030 should focus on:
- Products aligned with long-term national priorities
- Import substitution and localization opportunities
- Scalable and modular plant designs
- Strong vendor and customer integration
- Early adoption of quality and compliance standards
Manufacturing rewards patience, consistency, and execution excellence more than speed alone.
Long-Term Outlook for Indian Manufacturing Startups
The coming decade will separate opportunistic manufacturing from professionally built industrial enterprises. Indian manufacturing startups that think beyond short-term gains and invest in systems, quality, and technology will emerge as industry leaders.
Manufacturing is once again becoming aspirational in India—not just as a business, but as a nation-building activity. Entrepreneurs who act decisively during this window will help shape India’s position in global manufacturing value chains for decades to come.
How NIIR Project Consultancy Services (NIIR.org) Supports Entrepreneurs
Starting a manufacturing business requires structured planning and realistic assessment.
NIIR Project Consultancy Services (NIIR.org) assists entrepreneurs by preparing Market Survey Reports and Detailed Techno-Economic Feasibility Reports (DPRs) that cover:
- Manufacturing processes and technology selection
- Market demand and competitive analysis
- Plant layout, capacity, and utilities planning
- Machinery, raw materials, and manpower
- Project cost, profitability, IRR, and break-even analysis
NIIR’s DPRs are widely used for bank financing, investor evaluation, and government approvals, helping entrepreneurs make confident investment decisions.
Key Government Reference Portals
Entrepreneurs should regularly track updates from official sources:
- Ministry of Commerce & Industry – https://dpiit.gov.in
- Ministry of MSME – https://msme.gov.in
- Invest India – https://www.investindia.gov.in
- NITI Aayog – https://www.niti.gov.in
- Make in India – https://www.makeinindia.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why is 2025–2030 considered a golden period for manufacturing in India?
Because this period combines domestic demand growth, global supply-chain shifts, strong policy support, and rapid technology adoption.
Q2. Is this a good time for first-time manufacturing entrepreneurs?
Yes. Compared to the past, access to finance, policy clarity, and market opportunities are significantly better.
Q3. Which manufacturing sectors will grow the fastest?
Electronics, EVs, green energy equipment, specialty chemicals, engineering goods, agro-processing, and data-centre infrastructure.
Q4. How important is import substitution for startups?
Extremely important. Reducing imports creates assured domestic demand and long-term market stability.
Q5. Do startups need advanced technology to succeed?
Not always, but technology adoption improves efficiency, quality, and competitiveness over the long term.
Final Thought
The years 2025 to 2030 will represent a turning point in India’s industrial evolution. Manufacturing is no longer optional—it is becoming the backbone of economic growth, employment, and exports.
With strong policy alignment, expanding demand, global participation, and technological advancement, this decade offers a rare opportunity for entrepreneurs.
For those who plan carefully and execute professionally, this is not just a good time to enter manufacturing—it is the right time.



















