Spraying of micronutrients and crop protection have become vital for food security. Additionally, sustainable practices like managing soil fertility and balancing crop productivity have become inevitable in the present world. Among the numerous agrochemicals available in the world today, Sulphur WDG Manufacturing seems to be the most relevant to modern farming. This is because of its fungicidal and miticidal properties and also as an essential plant nutrient. As India and some other developing countries move toward Integrated Crop Management, the need for different forms of sulphur, especially WDGs, is increasing. These triggers entrepreneurial and MSME investments which make it easier for farm owners to leverage agrochemicals for expense management.
The goal of this article is to explore the demand and regulatory context of the Sulphur WDP industry alongside industrial innovation in the field, NPCS guidance, and project planning counseling from India’s best consulter to enable aspiring entrepreneurs from India with a full use case of planning and projecting implementation.
What Does Sulphur WDG Mean and Why is It Popular?
Sulphur WDG Manufacturing or Sulphur Water Dispersible Granules specifically caters to the needs of agriculture concerning crop protection and soil nourishment. With traditional formulations of sulhur like dust or wettable powder, there is always going to be the challenge of applying sulphur in a more environmentally-friendly way. However, WDG does not come with such negatives; it is a non-dusty, more effective form of elemental sulphur that dissolves evenly in water, yielding a delicate suspension fit for foliar sprays.
Sulphur WDG is comprised of almost 90% elemental sulphur granular form and is extensively utilized in different crops such as grape, paddy, cotton, pulses, oilseed, and citrus fruit. In addition, it helps with the control of powdery mildew and rust which are fungal diseases while providing essential sulpur nutrients for chlorophyll production in plants.
The recently published NPCS reports outline that the demand for sulphur-based formulations is increasing in both the domestic and international markets. One of the factors driving the growth for this segment is the focus given by the Indian government regarding the use of fertilizer and micronutrient fertilizers in the Soil Health Card Scheme. Furthermore, the increasing popularity of organic and sustainable farming has transitioned many farmers towards safer environment-friendly fungicides, whereSulphur WDG Manufacturing is a prime example.
Establishing the Foundation: Major Components Required for Sulphur WDG Manufacturing
Sulphur WDG Manufacturing begins with elemental sulfur powder, which must be at least 90% pure for optimal results. This component tends to be a byproduct of petroleum refining or natural gas processing. To achieve optimal dispersion and efficacy, the powdered sulfur must be ground to finer than 75 micron particle size.
In addition to chemical constituents, a number of non-chemical materials are also included to enhance the usability of the formulation. These include:
- Sulfurs dispersing agents aid in the uniform distribution of sulfur granules within water.
- Wetting agents, to improve water flow and suspension stability, and binders, which aid in granule formation during the granule forming stage.
- Anti-caking agents are used to minimize agglomeration during storage and movement.
- Clays and Kaolin provide fillers or carriers that give body to the formulation.
This combination of ingredients undergoes significant R&D to guarantee compatibility, stability, and adherence to the national agrochemical formulation standards for all agrochemical formulations.
Related: How to Start a Sulphur Powder Manufacturing Plant?
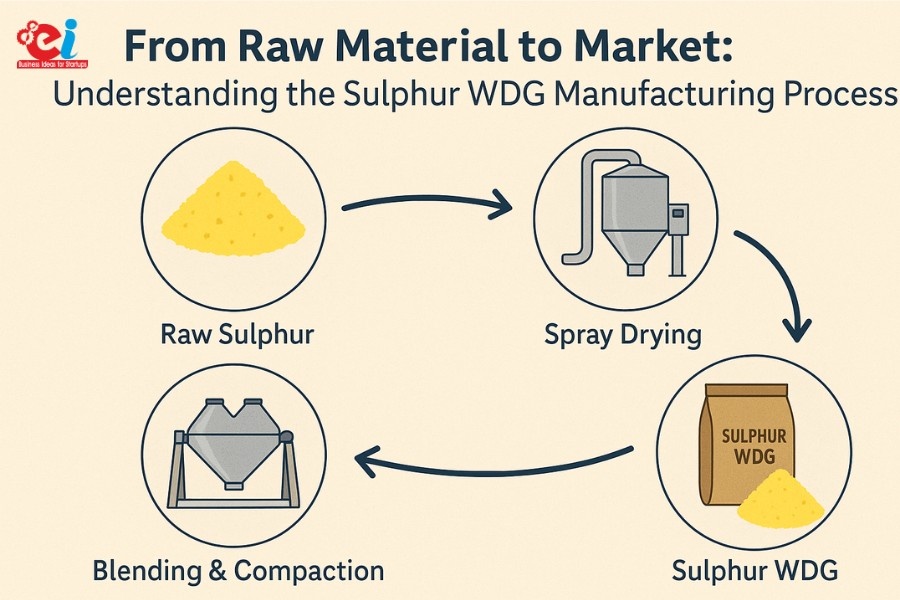
Manufacturing Process of Sulphur WDG: A Step-by-Step Overview
Industrial processes of Sulphur WDG manufacturing involves an intricate combination of chemical engineering and mechanical processes. The use of precision equipment with controlled environmental conditions assures repeatable product quality. Controlling environmental parameters guarantees uniform product quality.
1. Dry Blending
The process starts from blending the raw materials. In this stage, finely ground elemental sulphur is blended with suitable proportions of wetting and dispersing agents. The fined dry mix serves as the base of the formulation and its constancy and uniformity is important because it impacts the overall product’s dispersibility and stability.
2. Wet Granulation
After mariating the material through dry blending, further processing leads to the wet granulation stage. During this phase, a specific quantity of water or binder solution is added to the mixture in a high-shear mixer or granulator. The aim here is a damp mass that is cohesive without being overly wet. At this stage, the mixture begins to granulate into uniform sized and uniformly dense granules.
3. Extrusion and Pelletizing
The moist granules are subsequently sent to an extruder or pelletizer where they are formed into cylindrical or spherical pellets. These granules can be sized from 1 mm of 2 mm to increase ease of handling, and effective dispersion in water.
4. Drying
This is followed by drying, typically in a fluidized bed dryer or rotary dryer. The objective of drying is to remove excess moisture and harden the granules preparing them for storage and packaging.
5. Sieving and Grading
Once the granules have dried, they undergo sieving and grading processes to filter the preferred size granules. The granules that are too big are ground down and reused, while those that are too small are sent back to the wet mixing step.
6. Final Additions and Packaging
After being mixed with anti-caking agents, the product is subsequently packaged into moisture-proof pouches or laminated bags.
Every phase in the procedure must meet the policies set by FSSAI, CIBRC, and BIS (Indian Standard IS 3472). Plant setup requires the integration of quality control labs, where batch samples are analyzed for sulphur levels, dispersibility, particle size distribution, dust concentration, and pH balance.
Starting Sulphur Manufacturing Unit WDG: Infrastructure Investment
Building a plant for manufacturing Sulphur WDG is an industrial project of medium scale. It requires a scaled drawing, high grade stationary, and a workforce coupled with access to a steady supply of raw materials. Niir Project Consultancy Services estimates that with a detailed feasibility analysis, a plant that has a capability to produce between 5 and 10 tonnes daily will be set up with an investment of ₹5–10 crore considering the degree of automation, size, and location of the plant.
Key Infrastructural Elements Feature:
- Storage facilities for raw materials must be ventilated and compliant with hazardous materials regulations
- Pollution control equipment
- Vibratory sieving machines and dryers integrated into granulation units and pelletizers
- Research and Development laboratories to test quality control alongside pivotal dustless blending chambers
- Packaging machines, both form-fill-seal and manual, are included
NPCS provides elaborate technical drawings, DPR services, outlines, detailed project reports, and other plans which include designs for expanding plans for constructing new plants or expanding existing ones situated in different locations covering all aspects NPCS does. NPCS provides elaborate technical drawings, DPR services, and outlines, alongside detailed project reports, considering all aspects.
Environmental regulations issue a multidisciplinary set of rules pertaining to state and central standards concerning policing power requirements, water usage, and waste management systems.
Multifaceted boundaries control the industry and marketing of Sulfur WDG. A concrete example of these is the Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee (CIBRC) and the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) placing rules around basic safety and quality requirements crucial for any formulation to be utilized and marketed.
Operational standards must undergo approval by NPCS. Periodic control checkups verify internal quality benchmarks set requiring maintained minimal sulfur content of 90 percent, above 95 percent dispersibility, clear moisture content dip below 2 percent, and nonexistence of dust or particulate emissions, and pH neutrality to mildly acidic acidity.
Producing these, NPCS offers detailed compliance roadmaps, assist with applications, and use third party verifiers to ensure every batch builds up is up to in-house and overseas standard.
Anticipated Sulfur Market Trends
The global market for sulphur WDG is forecasted to grow more than 6% CAGR annually until 2030. In India, the highest demand is in horticultural and cereal cultivation states like Maharashtra, Gujarat, Punjab, and Karnataka. The growth of protected cultivation, high-value crop farming, and organic agriculture is increasing the demand for plant protection products containing sulphur.
Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America are emerging as some of the more significant sulfur WDG importers due to their growing agriculture sectors alongside lack of local manufacturing. There is plenty of opportunity for Indian manufacturers to export as long as they follow international phytosanitary and residue level standards.
How NPCS Can Help Entrepreneurs Enter the Sulphur WDG Market
With over three decades of expertise, Niir Project Consultancy Services (NPCS) offers unmatched support to entrepreneurs planning to establish their own Sulphur WDG manufacturing unit. Their consulting packages include:
- Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) specific to Sulphur WDG
- Market analysis and investment feasibility studies
- Machinery supplier contact lists and quotations
- Plant layout designs and process flow diagrams
- Raw material sourcing networks
- Financial planning, break-even analysis, and ROI forecasting
- Compliance and certification assistance (BIS, CIBRC, ISO)
NPCS also supports in preparing loan documentation for MSME funding, availing government subsidies, and getting investor presentations ready for angel investors or venture capitalists.
Conclusion: From Concept to Commercial Success
In 2025 and beyond, Sulphur WDG will continue to play a pivotal role in the future of agriculture. As farmers adopt better farming practices and governments emphasize on sustainable input usage, products like Sulphur WDG will enjoy steady and growing demand.
For entrepreneurs, this segment represents an opportunity that combines steady market demand, moderate capital investment, and export potential—all supported by government schemes and consultancy services from organizations like Niir Project Consultancy Services.
Whether you’re a first-time entrepreneur or an established agrochemical dealer planning forward integration, investing in a Sulphur WDG manufacturing unit could turn out to be a highly rewarding decision.
Explore NPCS Sulphur WDG Projects:
- Sulphur WDG Manufacturing Unit Setup (5–10 TPD)
- Agrochemical Formulation Plant Including Sulphur WDG
- Micronutrient and Bio-Fertilizer Unit with WDG Line
- Export-Oriented Sulphur WDG Processing Plant